Internationalization
This article collects all the resources you need to take advantage of Prismic's multi-language and localization feature when building a Nuxt.js website. This article is based on our multi-language example project. Feel free to download and use it.
Go to your Dashboard, select your Prismic repository's Settings > Translations and locales, and add all the languages you need. You can choose from the library of language codes or create a custom locale.
By default, the API will return content in your master language. Here's how to dynamically query alternate languages; in each example, we pass the language code to the query option from the URL.
You can query docs using the $prismic query helper. Look at the following example:
<script>
export default {
async asyncData({ $prismic, params, error }) {
const document = await $prismic.api.getByUID('post', params.uid, { lang: params.lang })
if (document) {
return { document }
} else {
error({ statusCode: 404, message: 'Page not found' })
}
}
}
</script>You can create localized routes for your dynamic pages and the homepage of your site. In the following example, we have two languages, English as the master locale and French as the second. Let’s see the routes we want to build:
For the homepage:
- English:
/ - French:
/fr-fr
For the dynamic pages, we want to use the lang code and the document's UID:
- English:
/about-us - French:
/fr-fr/a-propos-de-nous
Let’s go to the first step to create these routes.
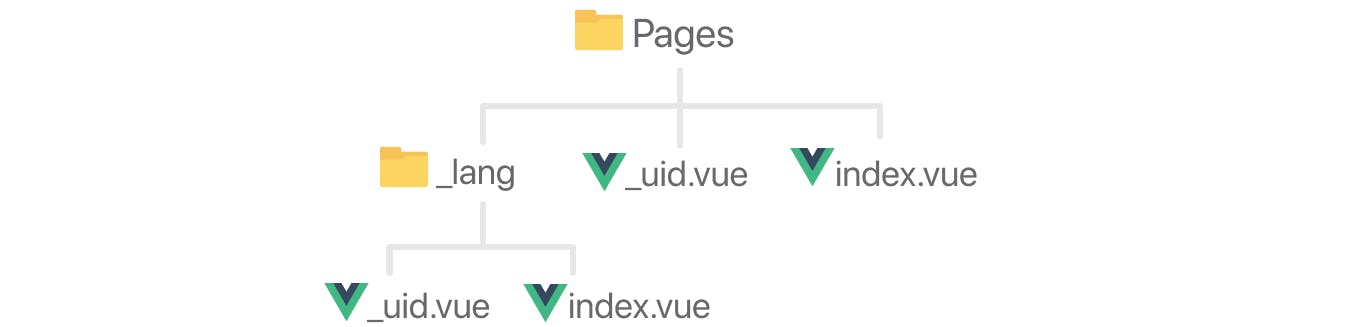
In Nuxt, files in the pages directory that are prefixed with an underscore _ generate dynamic pages.
Let's see the example. Inside /pages, the _lang folder will prepend the lang code to each route of the site. Inside that same folder, _uid.vue will create dynamic routes using the UID of our documents and index.vue the. homepage route.
Then, we'll import these two files in the other _uid.vue and index.vue at the same level as the _lang folder to have a version of the routes without the language code, in this case for English.
// import for one page to another
<script>
import _uid from '~/pages/_lang/_uid'
export default _uid
</script>Once your routes are created you will need to create internal links that lead to the right routes using a route resolver.
In these examples, we configure the routes so that the lang code is omitted from the route for the master language. (remember that the page types and master language en-us are example values. Modify them to match yours):
prismic: {
endpoint: "https://my-repo-name.cdn.prismic.io/api/v2",
apiOptions: {
routes: [
{
type: 'homepage',
path: '/:lang?,
},
{
type: 'page',
path: '/:lang?/:uid',
}
]
}
},Now you'll need to create a navigation button to switch between languages. We'll use the NuxtLink component to navigate between pages.
First, in the page query, get the alternate_languages value from the response and pass it as props to the lang switcher component (we'll create it in the next step). In this example, we're dynamically querying documents of the type 'Page'.
<template>
<div>
<lang-switcher :altLangs="altLangs"/>
<!-- Slices block component -->
<slices-block :slices="slices" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import LangSwitcher from "~/components/LangSwitcher.vue";
export default {
name: "page",
components: {
LangSwitcher,
},
async asyncData({ $prismic, params, error }) {
try {
// Languages from API response
let languages = $prismic.api.languages
// Setting Master language as default language option
let lang = { lang: languages[0].id }
// Query to get document content
const result = await $prismic.api.getByUID('page', params.uid, lang)
// Make an array of the IDs of the alternate language documents
const alternate_ids = result.alternate_languages.map((lang) => lang.id)
// Fetch the alternate language documents from the API
const altLangs = await $prismic.api.query(
$prismic.predicate.in('document.id', alternate_ids),
{ lang: '*' }
)
return {
// Document content (could also be `result.data.slices`
slices: result.data.body,
// Lang switcher
altLangs
};
} catch (e) {
// Returns error page
error({ statusCode: 404, message: "Page not found" });
}
}
};
</script>
In the /components folder, create a LangSwitcher.vue component and use the alternate languages passed to it to create a switch. This can be anything from a toggle, a select, or a button. For our example, we'll use a simple link that uses nuxt-link that will render the alternative language.
<template>
<section class="lang-switcher">
<nuxt-link v-for="altLang in altLangs" :key="altLang" :to="altLang.url">
<span>{{ altLang.lang }}</span>
</nuxt-link>
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ["altLangs"],
name: "lang-switcher",
};
</script>Can't find what you're looking for?
Need technical Support? Spot an error in the documentation? Get in touch with us on our Community Forum.