The Shift From SEO to AI Search: What Marketers Need to Know to Grow Organically in 2026
 By Lidija Kacar
By Lidija Kacar
Search is changing fast. People are no longer starting every question on Google. They ask ChatGPT. They research with Perplexity. They use Gemini’s new AI mode. And they expect a direct, personalized answer to a very specific question.
For marketing teams, the shift is already reshaping how organic growth works. The top-of-funnel traffic that once drove steady visibility is shrinking, while bottom-of-funnel visitors are more qualified than ever. At the same time, brands need more content, more variations, and more specificity than any manual workflow can support.
During a recent internal learning session, Prismic’s marketing team shared what this shift means for marketers and why scalable content creation is becoming non-negotiable. This article distills those insights into a clear, actionable guide you can use to adapt your organic strategy for both traditional search and AI search.
Key takeaways 🔑
- Traditional SEO isn't dead - it's evolving. Here's what's changing and what you need to know👇
- Search queries have grown from 6 words to 25+ words as users adopt conversational AI tools
- Zero-click answers mean visibility matters as much as traffic - track citations and mentions, not just clicks.
- The three pillars (on-page, off-page, technical) still apply, but the tactics within them are shifting.
- Content structure and volume requirements have outgrown manual workflows - teams need scalable solutions to compete.
- Bottom-of-funnel traffic remains strong while top-of-funnel queries are absorbed by AI search.
Bottom line: You need more specific content, faster production, and better tools to maintain organic growth in 2026.
SEO Is Evolving, Not Disappearing
At its core, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is still about helping people find the answers they need. Traditionally, this meant optimizing pages around keywords, mapping intent, and publishing content that aligns with what users type into Google.
That foundation still matters. As Edwina, Prismic’s Head of Marketing, shared, “AI search hasn’t killed SEO. It’s built on top of it.” Large Language Models (LLMs) still crawl the open web, still assess credibility, and still lean on authoritative sources to generate accurate answers.
The most significant change is where the discovery journey begins and how deeply users explore before ever landing on a website.
AI search hasn’t killed SEO. It’s built on top of it.
The Search Journey Starts Before Your Website
Instead of typing “best CMS 2026,” users now ask:
“What is the best CMS for a B2B scale up with a small marketing team that just raised a Series A?”
These conversational, context-rich requests require content that is equally specific and rich with detail. They are also five times longer than the average traditional keyword query. And because users can ask follow-up questions instantly, LLMs refine answers faster than traditional search engines ever could.
Tosin, Senior Growth Marketing Manager at Prismic, summed it up well: “The ability for individuals to deep-dive into a topic and do it much faster is greater with an LLM.”
This shift affects how users behave across search channels. As Daniel, on our growth team, shared, “We’re getting used to asking specific things in LLMs, so we’re going to see people doing that more in Google as well.”
Google seems to agree. Its new AI mode looks and feels like a chat interface. The line between LLMs and traditional search is blurring. The way we optimize needs to evolve with it.
The ability for individuals to deep-dive into a topic and do it much faster is greater with an LLM.
Visibility Matters as Much as Traffic
With AI search, users may get their answer without ever clicking through to a website. This is zero-click search in a new form: instead of snippets in Google, the answer surfaces directly inside ChatGPT or Gemini.
There are two ways your brand can appear in these answers:
- AI citations: when the model attributes information to your content and links to your site (typically when the search feature is enabled or search is triggered).
- AI mentions: when your brand name appears in the response without a link.
That means marketers must track visibility, not just traffic.
To show up in either, you need strong content. LLMs rely on the content they can access. If your content isn’t there, your competitors' content fills the gap. The model accepts that narrative as truth. This means your positioning is compromised long before anyone reaches your website.
Strong content helps you get cited by giving models clear, well-structured information they can confidently pull from. But showing up in both citations and mentions also requires brand authority across the web. This means reputable sites, experts, and communities must talk about you.
In other words, LLM visibility depends on two ingredients:
- Strong content that the model can rely on.
- Strong brand presence that the model recognizes.
As Tosin put it, “Credibility is a huge currency. It was huge in SEO, and it’s huge in AI search.”
SEO, AEO, GEO or AIO? The Naming Debate Is Still Ongoing

The industry is experimenting with new terminology:
- AIO (AI Optimization): This is often considered the broadest term, referring to the overall strategy of optimizing content and technical infrastructure for all forms of AI-driven discovery. This includes everything from using AI tools to automate content creation and technical audits to structuring data for machine readability.
- AEO (Answer Engine Optimization): This term is popular with those who see text-based answers as the primary output to optimize for. AEO focuses on structuring content to be directly cited within AI-generated answers, knowledge panels, and featured snippets. The goal is to win "zero-click" visibility by becoming the definitive, most accurate answer to a user's query, especially for voice search and AI Overviews.
- GEO (Generative Engine Optimization): Favored by some teams and marketers, GEO is seen as a more future-proof concept because it encompasses not just text, but also image and video results. This involves publishing deeply researched, authoritative content that can be used as a building block for AI-synthesized summaries.
Some other terms are popping up as well:
- AI SEO (Artificial Intelligence Search Optimization): Refers to creating and optimizing content for AI-powered search experiences. The term also captures a broader shift from traditional, reactive SEO toward predictive, AI-assisted strategies that anticipate user intent and future search behavior.
- LEO (LLM Engine Optimization): Focuses on building brand reputation so that large language models like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude actively recommend your brand as a trusted entity. This is about being endorsed by AI, not just cited.
- SXO (Search Experience Optimization): Emphasizes the user experience after the click as an important factor of optimizing for not only traffic but experience and conversions through optimized page speed, mobile design, and intent alignment.
- Search Everywhere Optimization: Yes, that's literally what it's called. A holistic approach that combines SEO, GEO, and AEO to ensure visibility across all platforms where users search, from Google to Reddit, TikTok, and AI chatbots.
As Daniel mentioned, "No single term has won yet." People are still trying to define the language around this space, and we don’t know which term will ultimately stick. At Prismic, we use GEO because we see it as a broader concept, one that, over time, will encompass far more than just answers or text.
What matters is not the acronym. It’s the strategy behind it.
Webinar: GEO experiments that actually drive visibility
Join us on December 11 at 4pm CET as Prismic’s Growth team and the CTO of Groundfog unpack what’s actually working in Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), what isn’t, and how to run simple, scalable tests that reveal why your pages show up or don’t in AI search.
The Three Pillars Still Apply: On-Page, Off-Page, and Technical
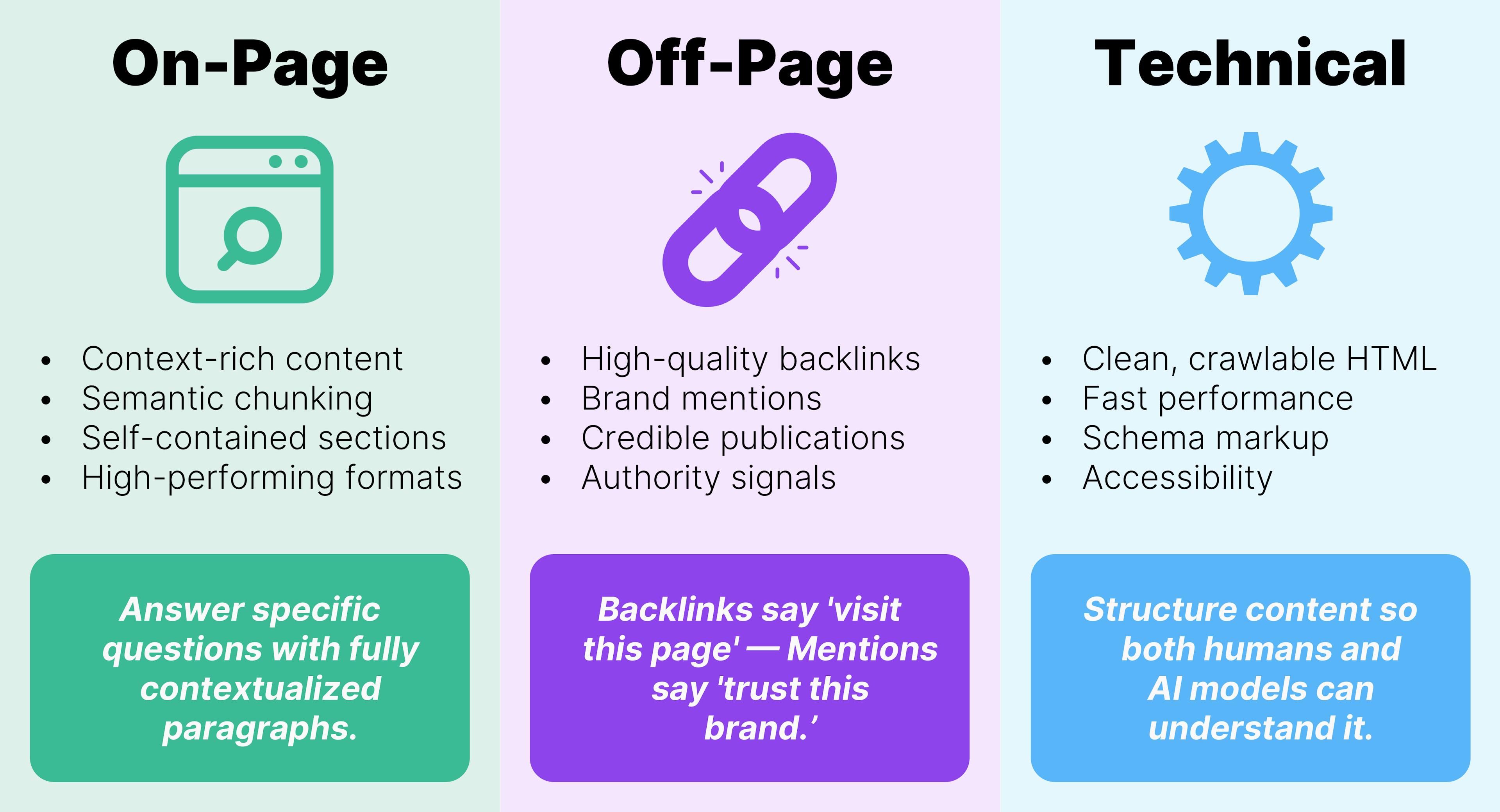
Even as search evolves, the core principles of optimization remain relevant.
On-Page
Users ask specific questions. LLMs pull structured, credible content. Companies need more pages that answer those questions in context.
Content should be well structured, clearly written and rich in contextual clues. One method gaining traction is semantic chunking, which means writing self-contained paragraphs that give an LLM enough information to surface your answer.
For example, instead of writing:
“Prismic helps teams build landing pages quickly.”
Consider a fully contextualized paragraph:
“Marketing teams often lose weeks waiting on developers to build or update landing pages. Prismic’s visual editor lets them create, publish, and optimize pages on their own, which removes engineering bottlenecks and dramatically speeds up content production.”
This gives the model enough detail to use your answer confidently.
To support this approach, structure pages so each section stands on its own. Group related ideas together and use layouts that naturally produce these context-rich “answer units.” This is semantic chunking through design, not just copywriting.
High-performing formats include:
- Comparison pages
- Listicles
- Help center articles
- Highly specific use-case or persona pages
- Detailed FAQs
These formats align well with the specificity of AI prompts. And if your website isn't the source of truth about your product or category, other sites will define it for you.
Off-Page
Off-page optimization is becoming increasingly important in optimizing your content for AI search. In classic SEO, the focus was mostly on backlinks: links from other websites pointing to yours. In the AI search era, backlinks are still useful, but they’re only part of the picture.
The other, increasingly important piece is mentions:
- A backlink tells a search engine, “this page is worth visiting.”
- A mention tells an LLM “this brand or page is trusted and relevant in this context.”
That citation might come from:
- A “Top 10 tools for X in 2026” article
- An in-depth review on a respected tech publication
- An industry report that uses your product or research as an example
- A thought-leadership piece where experts reference your brand
LLMs look at who is talking about you and where that conversation happens. High-authority publications and trusted industry sources carry far more weight than smaller sites, even if they do not link to you directly.
As Daniel put it during the session, “It’s better to be mentioned on CNN without a link than to have a link from a site considered less important.”
A strong off-page strategy in 2026 means:
- Continuing to earn relevant, high-quality backlinks
- Actively building brand mentions across credible publications
- Ensuring those external sources use accurate, up-to-date information from your website
Off-page signals essentially determine whether an LLM sees your brand as authoritative enough to include in its answers.
It’s better to be mentioned on CNN without a link than to have a link from a site considered less important.
Technical
Fast, accessible, and well-structured pages are still essential. Even though AI search feels new, LLMs still crawl and interpret websites in ways that are very similar to traditional search engines. They need clear structure, readable content, and pages that load quickly.
Technical optimization for AI search looks a lot like good technical SEO:
- Clean, crawlable HTML: LLMs rely on a clear hierarchy and semantic markup to understand context. Using proper headings, meaningful HTML elements, and logical structure helps models interpret your content consistently.
- Strong performance and accessibility: Fast load times, mobile-friendly design, and accessible markup (such as descriptive alt text and proper ARIA labels) help both users and AI systems. High-quality rendering and readability are still strong signals of trust.
- Structured data and Schema markup: Schema markup gives models explicit, machine-readable context. It makes key information easier for LLMs to interpret accurately, especially for elements like product FAQs, how-to steps, ratings and reviews, organizational details, and events. While Schema was originally adopted for enhancing Google search features, it also supports LLMs by clarifying meaning and reducing ambiguity. In a world where models extract answers directly from your page, structured data helps ensure the right information is surfaced.
- No shortcuts or hidden content: The temptation to create AI-only content or hide sections for crawlers will only harm long-term visibility. Search engines and AI models reward clarity, transparency, and genuinely helpful content.
The bottom line
You do not need a new technical playbook for AI search. You need a site that loads quickly, is easy to parse, and presents information in a structure that both humans and models can understand confidently. Schema markup and clean semantic structure help models interpret your content more accurately, while strong performance ensures a consistent experience across the board.
No, SEO Is Not Dead
Some marketers see declining traffic and assume SEO has run its course. As Edwina put it, “We like to call anything dead in marketing. But SEO is still important. We may have less web traffic from Google, yet people are still finding us in search and now through LLMs as well.”
The reality is more nuanced:
- Top-of-funnel definitions and general education queries are being absorbed by AI search.
- Bottom-of-funnel and purchase-intent queries still drive website visits.
If a user wants to buy something, they still end up on a website. That makes capturing high-intent searchers more important than ever.
This also means brands need more content that answers more specific questions. And that leads us to the real challenge.
The Structure and Volume of Content Required Has Outgrown Manual Workflows
Companies are already feeling the pressure:
- Teams want more organic traffic without relying entirely on paid ads.
- SEO teams can’t manually produce the proper structure and the volume of variations required for hundreds of long-tail, persona-specific queries.
- Marketing leaders see their existing SEO playbooks breaking as AI search grows.
As Edwina put it, “There are companies that have an organic content strategy but can’t keep up anymore with the volume required. They realize their strategy worked for Google but can’t scale for AI.”
This is where Prismic’s landing page builder becomes essential.
Why Marketers Are Turning to Prismic for SEO and GEO Landing Pages
Marketing teams need to create far more pages than they ever have before. Not generic templates. Not cookie-cutter location pages. They need hyper-specific content that matches how users now search.
Prismic makes that possible.
See how the Landing Page Builder works in under a minute:
Here's the process:
You upload a CSV with your variations and your base template. We help you scale landing pages that:
- Answer highly specific questions
- Target new long-tail opportunities
- Improve LLM visibility
- Scale without additional developers
- Maintain consistent brand quality
Teams are already using this to:
- Replace expensive paid acquisition with sustainable organic growth
- Launch pages tailored for specific locations
- Build industry, persona, and use-case specific pages at scale
- Publish entire GEO or SEO clusters in a fraction of the time
In a world where search continues to fragment, this level of scale is not optional. It is how you show up where buyers are asking their questions.
What You Should Do Next

If your team wants to grow organic traffic in 2026, focus on:
1. Build specific, context-rich content
Match the way people phrase questions in AI search.
2. Own your narrative
Keep your website updated so LLMs reference accurate information.
3. Track visibility, not just traffic
AI search may answer questions before users click.
4. Invest in scalable page creation
Manual SEO workflows cannot meet the volume modern search requires.
5. Use tools that accelerate production
A landing page builder designed for SEO and GEO helps you adapt instantly.
If you want to create pages at scale that actually rank in both traditional and AI search, Prismic can help you get there without adding writers or developers.
You need search pages that match how people search today. Upload your CSV and we’ll help you generate the thousands of variations you need to compete.